Added documentation for orchestration platforms (#3684)
parent
e3b627a192
commit
03937e7554
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ |
||||
# Minio on orchestration platforms [](https://slack.minio.io) [](https://goreportcard.com/report/minio/minio) [](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/) [](https://codecov.io/gh/minio/minio) |
||||
|
||||
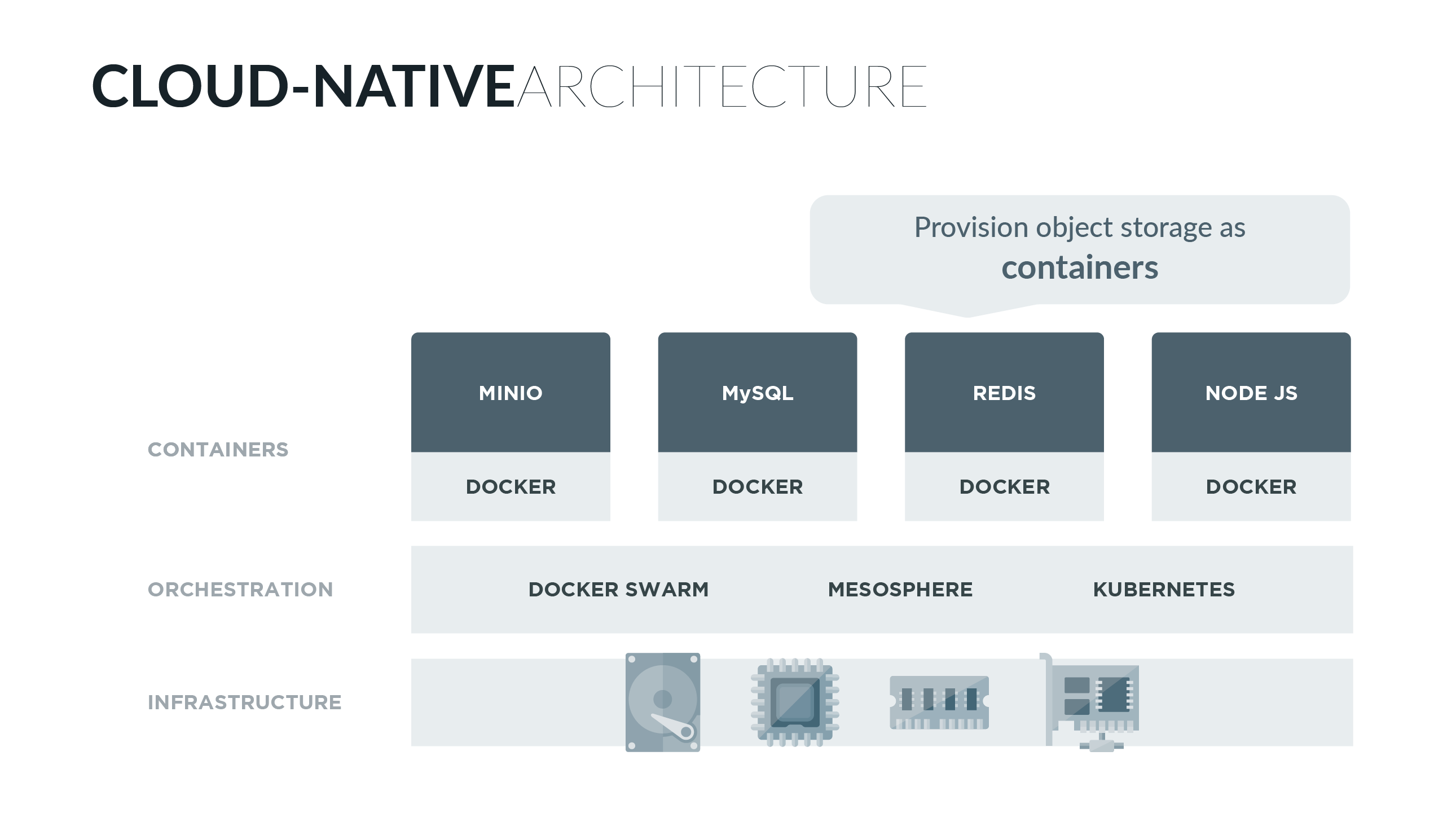
Minio is a cloud-native application designed to scale in a sustainable manner in multi-tenant environments. Orchestration platforms provide perfect launchpad for Minio to scale. Below is the list of documented orchestration platforms for Minio server: |
||||
|
||||
| Orchestration platforms| |
||||
|:---| |
||||
| [`Kubernetes`](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/minio/minio/master/docs/orchestration/kubernetes/README.md) | |
||||
| [`Docker Swarm`](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/minio/minio/master/docs/orchestration/docker-swarm/README.md) | |
||||
| [`DC/OS`](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/minio/minio/master/docs/orchestration/dcos/README.md) | |
||||
|
||||
## Why is Minio cloud-native? |
||||
The term cloud-native revolves around the idea of applications deployed as micro services, that can be scaled well. Its not about just retrofitting monolithic applications onto modern container based compute environment. A cloud-native application is portable and resilient by design, and can scale horizontally by simply replicating. Modern orchestration platforms like DC/OS, Kubernetes and Swarm make replicating and managing containers in huge clusters easier than ever. |
||||
|
||||
While containers provide isolated application execution environment, orchestration platforms allow seamless scaling by helping replicate and manage containers. Minio extends this by adding isolated storage environment for each tenant. |
||||
|
||||
Minio is built ground up on the cloud-native premise. With features like erasure-coding, distributed and shared setup, it focusses only on storage and does it very well. While, it can be scaled by just replicating Minio instances per tenant via an orchestration platform. |
||||
|
||||
> In a cloud-native environment, scalability is not a function of the application but the orchestration platform. |
||||
|
||||
In a typical modern infrastructure deployment, application, Database, Key-store, etc. already live in containers and are managed by orchestration platforms. Minio brings robust, scalable, AWS S3 compatible object storage to the lot. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@ |
||||
# Deploy Minio on DC/OS [](https://slack.minio.io) [](https://goreportcard.com/report/minio/minio) [](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/) [](https://codecov.io/gh/minio/minio) |
||||
|
||||
To deploy Minio on DC/OS, you can use a Universe package, or create a customized config file. We at Minio recently released an [official universe package](https://github.com/mesosphere/universe/tree/version-3.x/repo/packages/M/minio/0) to enable single click Minio deployment on a DC/OS cluster. |
||||
|
||||
## 1. Prerequisites |
||||
|
||||
- DC/OS 1.8 or later running on your cluster. |
||||
- [Marathon-LB](https://dcos.io/docs/1.8/usage/service-discovery/marathon-lb/usage/) installed and running. |
||||
- IP address of the public agent(s) where Marathon-LB or an available hostname configured to point to the public agent(s) where Marathon-LB is running. |
||||
|
||||
## 2. Setting up Minio |
||||
|
||||
You can install Minio Universe package using the DC/OS GUI or CLI. |
||||
|
||||
### Minio installation on DC/OS GUI |
||||
|
||||
Visit the DC/OS admin page, and click on `Univers` on the left menu bar. Then click on the `Package` tab and search for Minio. Once you see the package, click the `Instal` button on the right hand side. Then, enter configuration values like the storage and service type you’d like to use with your Minio instance. Finally enter the public Marathon-LB IP address under `networking >> public-agent`, and click `Review and Install`. |
||||
|
||||
This completes the install process. Before you can access Minio server, get the access key and secret key from the Minio container logs. Click on `Services` and select Minio service in DC/OS admin page. Then go to the `logs` tab and copy the accesskey and secretkey. |
||||
|
||||
### Minio installation on DC/OS CLI |
||||
|
||||
To install Minio package via CLI, type |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ dcos package install minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
## 3. Uninstalling Minio |
||||
|
||||
To uninstall Minio package via CLI, type |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ dcos package uninstall minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### Explore Further |
||||
- [Minio Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `mc` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `aws-cli` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `s3cmd` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `minio-go` SDK with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [The Minio documentation website](https://docs.minio.io) |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@ |
||||
# Deploy Minio on Docker Swarm [](https://slack.minio.io) [](https://goreportcard.com/report/minio/minio) [](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/) [](https://codecov.io/gh/minio/minio) |
||||
|
||||
Docker Engine provides cluster management and orchestration features in Swarm mode. Minio server can be easily deployed in distributed mode on Swarm to create a multi-tenant, highly-available and scalable object store. |
||||
|
||||
As of [Docker Engine v1.13.0](https://blog.docker.com/2017/01/whats-new-in-docker-1-13/) (Docker Compose v3.0), Docker Swarm and Compose are [cross-compatible](https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/#version-3). This allows a Compose file to be used as a template to deploy services on Swarm. We have used a Docker Compose file to create distributed Minio setup. |
||||
|
||||
## 1. Prerequisites |
||||
|
||||
* Familiarity with [Swarm mode key concepts](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/key-concepts/). |
||||
* Docker engine v1.13.0 running on a cluster of [networked host machines](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/swarm-tutorial/#/three-networked-host-machines). |
||||
|
||||
## 2. Create a Swarm |
||||
|
||||
SSH into the machine supposed to serve as Swarm manager. If the machine is named `manager`, you can SSH by |
||||
|
||||
```shell |
||||
docker-machine ssh manager |
||||
``` |
||||
After logging in to the designated manager node, create the Swarm by |
||||
|
||||
```shell |
||||
docker swarm init --advertise-addr <MANAGER-IP> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
After the manager is up, [add worker nodes](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/swarm-tutorial/add-nodes/) to the Swarm. Find detailed steps to create the Swarm on [Docker documentation site](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/swarm-tutorial/create-swarm/). |
||||
|
||||
## 3. Deploy distributed Minio services |
||||
|
||||
Download the [Docker Compose file](./docker-compose.yaml) on your Swarm master. Then execute the command |
||||
|
||||
```shell |
||||
docker stack deploy --compose-file=docker-compose.yaml minio_stack |
||||
``` |
||||
This deploys services described in the Compose file as Docker stack `minio_stack`. Look up the `docker stack` [command reference](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/stack/) for more info. |
||||
|
||||
After the stack is successfully deployed, you should be able to access Minio server via [Minio Client](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide) `mc` or your browser at http://[Node_Public_IP_Address]:[Expose_Port_on_Host] |
||||
|
||||
## 4. Remove distributed Minio services |
||||
|
||||
Remove the distributed Minio services and related network by |
||||
|
||||
```shell |
||||
docker stack rm minio_stack |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### Notes |
||||
|
||||
* By default the Docker Compose file uses the Docker image for latest Minio server release. You can change the image tag to pull a specific [Minio Docker image](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/). |
||||
|
||||
* There are 4 minio distributed instances created by default. You can add more Minio services (upto total 16) to your Minio Swarm deployment. To add a deployment |
||||
* Replicate a service definition and change the name of the new service appropriately. |
||||
* Add a volume in volumes section, and update volume section in the service accordingly. |
||||
* Update the command section in each service. Specifically, add the drive location to be used as storage on the new service. |
||||
* Update the port number to exposed for the new service. |
||||
|
||||
Read more about distributed Minio [here](https://docs.minio.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide). |
||||
|
||||
* By default the services use `local` volume driver. Refer to [Docker documentation](https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/#/volume-configuration-reference) to explore further options. |
||||
|
||||
* Minio services in the Docker compose file expose ports 9001 to 9004. This allows multiple services to run on a host. Explore other configuration options in [Docker documentation](https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/#/ports). |
||||
|
||||
* Docker Swarm uses ingress load balancing by default. You can configure [external load balancer based](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/ingress/#/configure-an-external-load-balancer) on requirements. |
||||
|
||||
### Explore Further |
||||
- [Minio Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `mc` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `aws-cli` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `s3cmd` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `minio-go` SDK with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [The Minio documentation website](https://docs.minio.io) |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@ |
||||
version: '3' |
||||
|
||||
services: |
||||
minio1: |
||||
image: minio/minio:RELEASE.2017-01-25T03-14-52Z |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- minio1-data:/export |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "9001:9000" |
||||
networks: |
||||
- minio_distributed |
||||
environment: |
||||
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE |
||||
MINIO_SECRET_KEY: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY |
||||
deploy: |
||||
restart_policy: |
||||
delay: 10s |
||||
max_attempts: 10 |
||||
window: 60s |
||||
command: server http://minio1/export http://minio2/export http://minio3/export http://minio4/export |
||||
|
||||
minio2: |
||||
image: minio/minio:RELEASE.2017-01-25T03-14-52Z |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- minio2-data:/export |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "9002:9000" |
||||
networks: |
||||
- minio_distributed |
||||
environment: |
||||
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE |
||||
MINIO_SECRET_KEY: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY |
||||
deploy: |
||||
restart_policy: |
||||
delay: 10s |
||||
max_attempts: 10 |
||||
window: 60s |
||||
command: server http://minio1/export http://minio2/export http://minio3/export http://minio4/export |
||||
|
||||
minio3: |
||||
image: minio/minio:RELEASE.2017-01-25T03-14-52Z |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- minio3-data:/export |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "9003:9000" |
||||
networks: |
||||
- minio_distributed |
||||
environment: |
||||
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE |
||||
MINIO_SECRET_KEY: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY |
||||
deploy: |
||||
restart_policy: |
||||
delay: 10s |
||||
max_attempts: 10 |
||||
window: 60s |
||||
command: server http://minio1/export http://minio2/export http://minio3/export http://minio4/export |
||||
|
||||
minio4: |
||||
image: minio/minio:RELEASE.2017-01-25T03-14-52Z |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- minio4-data:/export |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "9004:9000" |
||||
networks: |
||||
- minio_distributed |
||||
environment: |
||||
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE |
||||
MINIO_SECRET_KEY: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY |
||||
deploy: |
||||
restart_policy: |
||||
delay: 10s |
||||
max_attempts: 10 |
||||
window: 60s |
||||
command: server http://minio1/export http://minio2/export http://minio3/export http://minio4/export |
||||
|
||||
volumes: |
||||
minio1-data: |
||||
|
||||
minio2-data: |
||||
|
||||
minio3-data: |
||||
|
||||
minio4-data: |
||||
|
||||
networks: |
||||
minio_distributed: |
||||
driver: overlay |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@ |
||||
# Deploy Minio on Kubernetes [](https://slack.minio.io) [](https://goreportcard.com/report/minio/minio) [](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/) [](https://codecov.io/gh/minio/minio) |
||||
|
||||
Kubernetes constructs like Deployments and StatefulSets provide perfect platform to deploy Minio server in standalone, distributed or shared mode. In addition, using Minio [Helm](https://helm.sh) Chart, you can deploy Minio server with a single command on your cluster. |
||||
|
||||
Minio Helm Chart offers great deal of [customizability](#configuration), still if you'd rather like to deploy Minio using custom config files, you can do that as well. This [blog post](https://blog.minio.io/build-aws-s3-compatible-cloud-storage-on-gcp-with-minio-and-kubernetes-159cc99caea8#.8zesfh6tc) offers an introduction to running Minio on Kubernetes using .yaml configuration files. |
||||
|
||||
## 1. Prerequisites |
||||
|
||||
* Kubernetes 1.4+ with Beta APIs enabled for default standalone mode. |
||||
* Kubernetes 1.5+ with Beta APIs enabled to run Minio in [distributed mode](#distributed-minio). |
||||
* PV provisioner support in the underlying infrastructure. |
||||
* Helm package manager [installed](https://github.com/kubernetes/helm#install) on your Kubernetes cluster. |
||||
|
||||
## 2. Deploy Minio using Helm Chart |
||||
|
||||
Install Minio chart by |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
Above command deploys Minio on the Kubernetes cluster in the default configuration. Below section lists all the configurable parameters of the Minio chart and their default values. |
||||
|
||||
### Configuration |
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Description | Default | |
||||
|----------------------------|-------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------| |
||||
| `image` | Minio image name | `minio/minio` | |
||||
| `imageTag` | Minio image tag. Possible values listed [here](https://hub.docker.com/r/minio/minio/tags/).| `RELEASE.2017-01-25T03-14-52Z`| |
||||
| `imagePullPolicy` | Image pull policy | `Always` | |
||||
| `mode` | Minio server mode (`standalone`, `shared` or `distributed`)| `standalone` | |
||||
| `numberOfNodes` | Number of nodes (applicable only for Minio distributed mode). Should be 4 <= x <= 16 | `4` | |
||||
| `accessKey` | Default access key | `AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE` | |
||||
| `secretKey` | Default secret key | `wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY` | |
||||
| `configPath` | Default config file location | `~/.minio` | |
||||
| `mountPath` | Default mount location for persistent drive| `/export` | |
||||
| `serviceType` | Kubernetes service type | `LoadBalancer` | |
||||
| `servicePort` | Kubernetes port where service is exposed| `9000` | |
||||
| `persistence.enabled` | Use persistent volume to store data | `true` | |
||||
| `persistence.size` | Size of persistent volume claim | `10Gi` | |
||||
| `persistence.storageClass` | Type of persistent volume claim | `generic` | |
||||
| `persistence.accessMode` | ReadWriteOnce or ReadOnly | `ReadWriteOnce` | |
||||
| `resources` | CPU/Memory resource requests/limits | Memory: `256Mi`, CPU: `100m` | |
||||
|
||||
You can specify each parameter using the `--set key=value[,key=value]` argument to `helm install`. For example, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --name my-release \ |
||||
--set persistence.size=100Gi \ |
||||
stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
The above command deploys Minio server with a 100Gi backing persistent volume. |
||||
|
||||
Alternately, you can provide a YAML file that specifies parameter values while installing the chart. For example, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --name my-release -f values.yaml stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### Distributed Minio |
||||
|
||||
This chart provisions a Minio server in standalone mode, by default. To provision Minio server in [distributed mode](https://docs.minio.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide), set the `mode` field to `distributed`, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set mode=distributed stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
This provisions Minio server in distributed mode with 4 nodes. To change the number of nodes in your distributed Minio server, set the `numberOfNodes` field, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set mode=distributed,numberOfNodes=8 stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
This provisions Minio server in distributed mode with 8 nodes. Note that the `numberOfNodes` value should be an integer between 4 and 16 (inclusive). |
||||
|
||||
#### StatefulSet [limitations](http://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/abstractions/controllers/statefulsets/#limitations) applicable to distributed Minio |
||||
|
||||
* StatefulSets need persistent storage, so the `persistence.enabled` flag is ignored when `mode` is set to `distributed`. |
||||
* When uninstalling a distributed Minio release, you'll need to manually delete volumes associated with the StatefulSet. |
||||
|
||||
### Shared Minio |
||||
|
||||
To provision Minio servers in [shared mode](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/shared-backend/README.md), set the `mode` field to `shared`, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set mode=shared stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
This provisions 4 Minio server nodes backed by single storage. To change the number of nodes in your shared Minio deployment, set the `numberOfNodes` field, |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set mode=shared,numberOfNodes=8 stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
This provisions Minio server in shared mode with 8 nodes. |
||||
|
||||
### Persistence |
||||
|
||||
This chart provisions a PersistentVolumeClaim and mounts corresponding persistent volume to default location `/export`. You'll need physical storage available in the Kubernetes cluster for this to work. If you'd rather use `emptyDir`, disable PersistentVolumeClaim by: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set persistence.enabled=false stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
> *"An emptyDir volume is first created when a Pod is assigned to a Node, and exists as long as that Pod is running on that node. When a Pod is removed from a node for any reason, the data in the emptyDir is deleted forever."* |
||||
|
||||
## 3. Uninstalling the Chart |
||||
|
||||
Assuming your release is named as `my-release`, delete it using the command: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm delete my-release |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
The command removes all the Kubernetes components associated with the chart and deletes the release. |
||||
|
||||
### Notes |
||||
|
||||
* An instance of a chart running in a Kubernetes cluster is called a release. Helm automatically assigns a unique release name after installing the chart. You can also set your preferred name by: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --name my-release stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
* To override the default keys, pass the access and secret keys as arguments to helm install. |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
$ helm install --set accessKey=myaccesskey,secretKey=mysecretkey \ |
||||
stable/minio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### Explore Further |
||||
- [Minio Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `mc` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [Use `aws-cli` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `s3cmd` with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio) |
||||
- [Use `minio-go` SDK with Minio Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide) |
||||
- [The Minio documentation website](https://docs.minio.io) |
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 74 KiB |
Loading…
Reference in new issue